
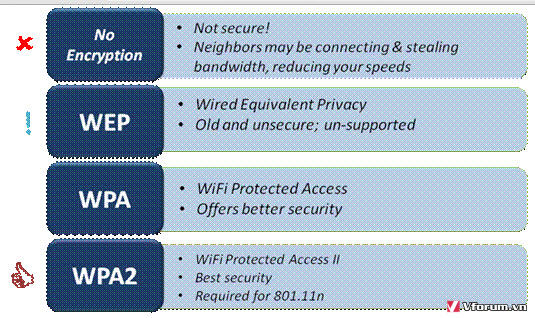
It wasn’t long before a new technology called WPA, or Wi-Fi Protected Access debuted to address many of WEP’s shortcomings. Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) Address WEP’s Shortcomings After spending less than a minute intercepting data (fewer than 100,000 packets in all) they were able to compromise a WEP key in just three seconds. Researchers in the computer science department of a German university recently demonstrated the capability to compromise a WEP-protected network very quickly.
WIFI WEP VS WPA PLUS
The process of ‘cracking’ a WEP key used to require that a malicious hacker intercept millions of packets plus spend a fair amount of time and computing power. As a result, most people just set up a single key and then continue using it ad infinitum.Įven worse, for those that do change the WEP key, new research and developments reinforce how even changing WEP keys frequently is no longer sufficient to protect a WLAN. But few bother to do this because changing WEP keys is inconvenient and time-consuming because it has to be done not just on the router, but on every device that connects to it. This problem used to be something you could mitigate by periodically changing the WEP key (which is why routers generally allow you to store up to four keys).

But the fact that packets are encrypted doesn’t prevent them from being intercepted, and due to some esoteric technical flaws it’s entirely possible for an eavesdropper to intercept enough WEP-encrypted packets to eventually deduce what the key is. When you set up a router with a WEP encryption key, that one key is used by every device on your network to encrypt every packet that’s transmitted. WEP’s major weakness is its use of static encryption keys. WEP is used at the two lowest layers of the OSI model – the data link and physical layers it therefore does not offer end-to-end security. However, it has been found that WEP is not as secure as once believed. WEP was the encryption scheme considered to be the initial standard for first generation wireless networking devices. WEP provides security by encrypting data over radio waves so that it is protected as it is transmitted from one end point to another. Because wireless networks broadcast messages using radio, they are susceptible to eavesdropping. Short for Wired Equivalent Privacy (or Wireless Encryption Protocol), WEP is part of the IEEE 802.11 wireless networking standard and was designed to provide the same level of security as that of a wired LAN. Wireless Encryption Protocol (WEP) Explained

When protecting data send via wireless, security and protection is offered through encryption schemes that come with your wireless hardware you can enable. When using a wireless access point or router it is important to remember that if you can send information from one device and receive it at another, anyone else within range might also be able to receive it. WPA has been a mainstream technology for years now, but WEP remains a standard feature on virtually every wireless router on store shelves today.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
